OSPF Routing Protocol
Abstract:
The report discusses the OSPF
Routing protocol and its implementation in networks. There are different
routing protocols supported by modern communication devices but how OSPF stands
out as a unique protocol will be discussed in the report. OSPF is a
dynamic routing protocol developed by IETF International Engineering Task Force
in 1989. OSPF uses a link-state algorithm known as the Dijkstra algorithm. The algorithm
uses a mechanism to find the shortest path between the source and the destination.
In link state routing the network topology and cost of all links are known.
These link state packets are broadcasted to all the connected nodes in the
network. OSPF divides the networks into different administrative domains called
Areas. The reason behind this logical network division is to reduce the broadcasting
in the whole network by limiting it to a specific group. OSPF grouping
reasonably reduces the troubleshooting problems by confining each update or issue
to the same area. In a bigger OSPF network, there can be multiple Areas these
areas must be centrally connected to the Backbone or Area 0 network. This is Area
0 that helps in exchanging information between the other Areas and the concept
is called Multi Area OSPF.
Introduction:
Routing is a layer-III concept in
which information on routes is exchanged between different networks. The route
information exchange between different networks is achieved by either adding
the required manually or we use any protocol to do that. The concept of manual
addition of routes to a router is called static routing and the routing
exchange achieved by using a protocol is called dynamic routing.
OSPF is an interior gateway dynamic
routing protocol that is used to exchange routing information between different
networks but within the same Autonomous System. OSPF is one of the IP routing
protocols that work on port number 89. For the initial database setup, it uses
broadcasting on the IP address 224.0.0.5. The link state algorithm of OSPF
collects link state information from all the connected networks which is called
the link state database. OSPF advertises the directly connected networks for
routing information exchange, after successful advertisement OSPF neighborships
are established between the devices through which routing information’s exchanged.
OSPF is best suited for large complex
networks that contain many sub-networks. These sub-networks are divided into
Areas and all areas must be connected to Area0 for successful communication. Unlike
RIP and other routing protocols, OSPF only shares the change that occurred in a
network it doesn’t share any information with its neighbors when everything is
running smoothly.
OSPF
Operations
OSPF is a link-state
routing protocol that is the most loved and famous enterprise network protocol. It
is one of the best available Interior gateway protocols due to its unique
features.
When OSPF is configured
in a network for the first time, OSPF-enabled routers start listening to the neighbor
OSPF-enabled routers for the collection of links state information. This link state
information is gathered through the interfaces that connect one router to
another OSPF router. At the end of the listening phase, the OSPF router saves the information
to a database called link state database or LSDB. After gathering link state
database information,
the OSPF router runs the
Dijkstra algorithm or shortest path first (SPF) to convert the link state
database to three different tables. One of the tables will be the one used for the shortest path calculation from the router to the destination network.
The OSPF operations can
better be demonstrated using the below network diagram. Here we are having two
networks connected to R1 and R5 and traffic has been generated from PC-A to
PC-B. But before that OSPF routing protocol has been configured on the routers.
All the routers in the below network belong to Area 0. Soon after the OSPF
configuration, every router will try to find the neighboring router through the
interface connecting to the neighboring router.
During this process, the
OSPF routers will form neighboring adjacencies by going through different
stages. Every router will form a neighbor adjacency with the other connected
OSPF routers. After adjacencies, the router try to find the best path to PC-B from PC-A. OSPF cost of all the paths that connect it with Network PC- B. Based on this path cost
OSPF router selects the best path towards the target network. The path having the lowest
cost is considered the best path.
In the above scenario, the
PC-A has 15+ paths and OSPF will select the best path by calculating the cost
of each interface.
Based on the interface cost
of interfaces, the router R1 will select the highlighted path of the PC-A
traffic because the highlighted interface has the lowest cost. This is the best
network route and the OSPF router will keep this routing information in the routing
table. The routing will not change until and unless any change occurs in the
network.
If any link between R1
and R5 doesn’t break path will remain the same but when a link failure occurs, OSPF
will again run the Dijkstra algorithm to find the next best available path in the
above diagram the values shown with each link is the link cost. The link cost
is calculated with the formula below.
cost = reference bandwidth / interface bandwidth
Here cost of the interface is
calculated by dividing the reference bandwidth by the bandwidth of an OSPF-enabled interface. Below is the reference chart for OSPF costs.
|
Interface |
Bandwidth |
OSPF Cost |
|
Gigabit Ethernet |
1 Gbps |
1 |
|
Fast Ethernet |
100 Mbps |
1 |
|
Ethernet |
10 Mbps |
10 |
|
E1 |
2 Mbps |
48 |
|
T1 |
1.55 Mbps |
64 |
Advantages
of Configuring OSPF In a Network
·
There are no hop limitations in OSPF like we
have in some other protocols like RIP and IGRP.
·
OSPF has a very fast convergence and calculates the next path in instants when the PR path goes down.
·
It divides the administrative networks into
different areas for easy management and Maintenance.
·
Provides the effective use of VLSM.
·
Supports load balancing, Active and backup
configurations.
OSPF
Implementation and Configuration
OSPF protocol is used for
large networks where network reliability, network Scalability, network
redundancy is, and load balancing is valued. The implementation of OSPF in an
enterprise network provides us with the above advantages.
When the OSPF is
configured for networks that have a single group we call it single Area OSPF and
when the network is a combination of many groups such a network is called Multi
Area OSPF. In the below network we will configure a multi-area network OSPF
network and analyze the routing tables.
The above network of multiple paths when a
packet travels from PC1 to PC2. The packet has three paths when it reaches R1. The paths have different costs due to different types of cables. The top path
is having a longer path due to the number of routers in between but it is using
fast ether cable which has a lower cost. The second path is a serial cable-based
path which is the shortest path in the network. The last path is also a serial
cable-based path. The routing table is then installed according to the shortest
and best path. Each router has a database received from the connected router for the formation of routing table.
Each OSPF router is
identified with a router ID which is an IP address and is the highest IP address of this router and
being used for identification in the network.
For successful routing information,
OSPF enabled router to establish neighborship adjacencies which can be queried as below. The neighbor ids are the routers with which this router has
established neighborship relations.
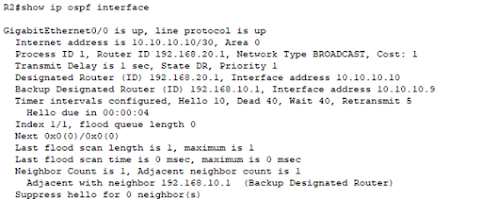
All routers keep checking
the neighborship adjacencies by sending hello and keep alive packets. They are
set to a specific value and every OSPF router should follow these values for
establishing adjacencies. If the hello, dead timer between two routers is not the same, the routers can’t exchange routing information between them. We can
confirm the hello and dead time by querying the information of OSPF enabled router
interface.
Now Let’s check which
path the packet are choosing here when they arrive from the PC-A. The router
routing table can be queried to check the status of router of the network 2.
We are receiving the
required network 2 routers on R1 through the gigabit Ethernet0/0 which is
connected to the top router which is the best path. If this path gets down the
router R1 will select the next best path.
Authentication
in OSPF
One of the best features
that OSPF offers is the authentication that is done to secure the routing
updates between OSPF routers. OSPF supports two types of authentication plain
text authentication and encrypted MD5 authentication. For the proper function
of authentication methodology, all routers should be enabled with the same
authentication mechanism.
The
Concept of OSPF Virtual Links
One of the mechanisms of
OSPF usage is in the formation of Areas and connection of all Areas with the
backbone Area or Area 0. But in the case were there is not possible to connect
other areas with the backbone areas. In such cases, still, the other Areas are connected to area 0 through some workaround to build a logical connection with area 0. This mechanism of virtual
connectivity is via OSPF virtual links.
OSPF
Table Types
OSPF maintains three
types which are below.
·
Neighbour Table: Information of OSPF neighbors.
·
Topology Table: Information about the whole
topology
·
Routing Table: List of the best route to
different networks.
Conclusion
This report discusses the
OSPF routing protocol, its implementation in a network, and the configuration
steps with advantages. It also discusses the OSPF operations and convergence
with the failure testing. We have developed a scenario where we have multiple
paths from source to destination and the selection of the best path. We also
tested when the best path gets unavailable and how OSPF selects the second-best
path. The OSPF cost factor is one of the important factors that can be used for
manipulation of the best path and checking the type of interfaces that have different
costs and the formula used for cost calculation. On its advantages and other good features, it stands out as one of the best protocols and most used
protocols for enterprise networks.