OSI Model – Introduction
Open system interconnection is abbreviated as OSI, which is a
networking standard protocol suite. Before the development of the ISO model in the
1970s, every vendor was producing devices with their own standards which caused
interoperability issues. Therefore, the international standardization
organization felt a need for introducing a standard manufacturing model for all
vendors. This was the basis for OSI model development to avoid interoperability
issues.
Layers of the OSI Model
The beauty of the OSI model is this it covers the whole
communication process from the end devices to other end devices. The whole
communication process has been divided into seven layers. Each layer has its
own function supporting communication.
Below are the seven layers of the OSI Model
·
Application
Layer
·
Presentation
Layer
·
Session
Layer
·
Transport
Layer
·
Network
Layer
·
Data
link layer
·
Physical
Layer.
Functions Of OSI Layers
Each OSI layer is associated with a specific function for the
delivery of data from source to destination.
Application Layer
This is the layer that provides an interface for the user to
interact with an application that initiates a communication process. We have a number of tasks that fall in the
application layer like remote access of devices, resource sharing between machines,
and the management of networks.
Presentation Layer
The presentation layer is the sixth layer in the list of OSI
model layers. This layer is used to translate the user input to the machine
language. It also performs the functions of data encryption and data
compression for transmission.
Session Layer
The session layer is associated with establishing sessions
between the source and destination. The job of establishing a session before
data transfer and session termination upon data transfer is performed by the session
layer. At the same time, this layer can establish multiple sessions with
different destinations.
Transport layer
The transport layer is responsible for the successful and
reliable delivery of data from the source to the destination. This layer works based
on logical ports that are used to create sockets when combined with the IP
address. Based on this socket, the data specified is differentiated.
Network Layer
The network is the third layer of this model which is used
for logical addressing of network devices. Devices are addressed using the IP
protocol and routers perform the function of packet forwarding after finding
the location of devices in the networks.
Data Link Layer
This layer corrects the errors that occur at the physical
layer and put the frames on the physical layer. This layer reads the MAC
address and delivers frames in the Local Area Networks. This layer is further
divided into the MAC layer and LLC.
Physical Layer
The physical layer is layer 1 that is referred to the physical
devices in the network that carries traffic in the form of bits. The
connectors, cables, and hubs are called layer 1 devices. This is the layer
where devices are connected with each other.
The functions of the seven layers have been summarized below showing their main functions against each layer
Transmission Technologies
Transmission is the process of sending signals between a
source and a destination. Through these signals, information is transmitted in
digital or analog format. Different type of protocols is used for this transfer
of information like the modulation process demodulation, coding, decoding,
multiplexing, and demultiplexing.
We have two main mediums of transmission that are
·
Wireless
Media or Broadcast Networks
·
Wired
media or point-to-point networks
Wireless Media or Broadcast Networks
This is a type of transmission technology where the data or
information is transmitted over wireless media. There is no dedicated
connection between the source and destination nodes. In this case, the data
transmitted by one node is received by all other nodes. The requirement of
information transfer in this type of communication is the reception of the
signals transmitted by the main broadcasting device and the connecting devices
are authenticated and a connection is made. After the connection is made the
information can be exchanged.
The above figure shows a broadcast network where the router is a WI-FI router that generates signals which are received by the end devices and connectivity is established.
Wired /Point to Point Networks
In this technology, we have dedicated physical connections
between devices. The data can be exchanged between these devices only. There may be intermediate devices
connecting them, but this
connection should be a physical cable, fiber, etc.
The point-to-point communication is established for sensitive
data, which can be either voice, data, video, etc. but security bears great
importance in this case.
Wired communication is also important when the bandwidth
requirement is high as wireless signals may get weaker after going through
certain obstructions
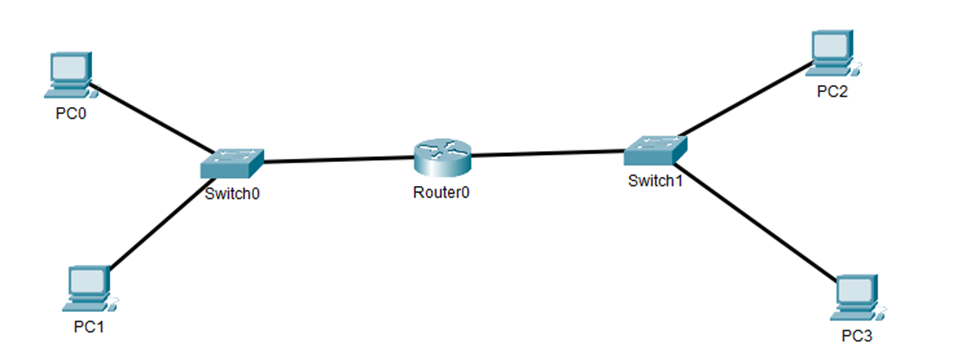
The below figure shows how wired devices are connected.
Comparison
between Wireless and Wired Technologies
|
Wired
Technology |
Wireless
Technology |
|
Physical
Media Exist |
No
need of Physical media |
|
No
antenna is required |
Antenna
is required |
|
Electrical
or optical signals are sent |
Electromagnetic
waves are used. |
|
More
suitable for short-distance communication |
Suitable
for large distance communication |
|
Less
Complex for deployment |
more
complex for deployment |
|
Supports
high Bandwidth |
Supports
less Bandwidth |
|
Less
reliable, cable damage issues |
Reliable,
no damage issues |
|
Faster
than Wireless |
Slower
than wired technology |





No comments:
Post a Comment